Blockchain Basics: Understanding Its Impact on Digital Security
Blockchain technology has garnered significant attention over the past few years, revolutionizing the way we think about data security and digital transactions. Originally developed to support cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved into a powerful tool for ensuring digital security in various industries. This guide will break down the basics of blockchain technology and explore how it’s transforming digital security.
1. What is Blockchain?
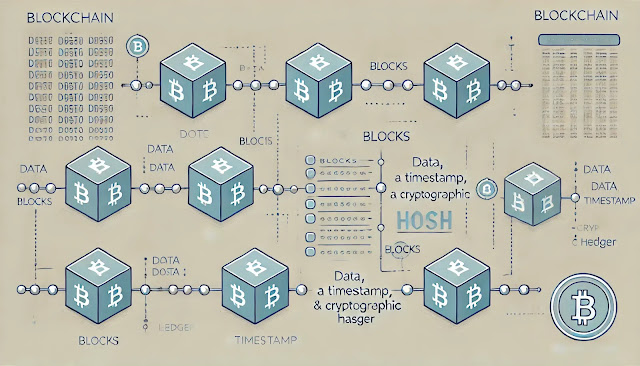
At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. This ledger is structured as a chain of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. Here’s a simple breakdown of how blockchain works:
- Blocks: Each block stores a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a unique identifier known as a hash. The hash of the previous block is also included, creating a chain that links each block to the one before it.
- Decentralization: Instead of a central authority (like a bank) managing the ledger, blockchain relies on a network of computers (nodes). Each node holds a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring transparency and security.
- Consensus Mechanisms: To add a new block to the chain, network participants must agree that the transaction is valid. This is usually achieved through consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
2. Key Features of Blockchain for Digital Security
Blockchain’s unique features make it a highly secure and reliable technology for digital transactions. Here’s what makes it stand out:
a. Immutability
Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete. Each block is linked to the previous one, and altering a block would require changing all subsequent blocks, which is computationally impractical. This immutability ensures that records remain tamper-proof, creating a trustworthy environment for transactions.
b. Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain offers transparency since all network participants have access to the entire ledger. Every transaction is time-stamped and recorded, allowing anyone to trace the history of a particular asset. This traceability is crucial in sectors like supply chain management, finance, and healthcare, where data integrity and provenance are paramount.
c. Decentralization
Traditional databases are centralized, relying on a single authority to manage and validate transactions. In contrast, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, where no single entity controls the data. This decentralization significantly reduces the risk of hacking and data breaches, as there is no single point of failure.
d. Encryption and Cryptography
Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one using a cryptographic hash, making it extremely difficult to alter information. Digital signatures and private keys further enhance the security by ensuring that only authorized parties can access or modify the data.
3. How Blockchain Enhances Digital Security
Blockchain is reshaping the digital security landscape by providing new ways to secure data, verify identities, and protect sensitive information. Here’s how it impacts various sectors:
a. Financial Services
Blockchain is transforming the financial industry by enabling secure, peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. With blockchain, transactions are verified and recorded in a public ledger, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft. Smart contracts – self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code – further enhance security by automating transactions based on pre-defined conditions.
b. Cybersecurity
Blockchain's decentralized nature makes it an ideal solution for cybersecurity challenges. It helps secure sensitive data, like personal information, by encrypting and distributing it across the network. This makes data virtually immune to hacking, as altering one part of the data would require altering every copy on the network.
c. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain enables transparent tracking of goods from their origin to the end consumer. Every transaction and movement of goods is recorded in real-time on the blockchain, allowing for verification and reducing the risk of counterfeit products. This transparency enhances the security of supply chains, ensuring that only authentic and quality products reach consumers.
d. Digital Identity Management
Traditional identity management systems are prone to data breaches and identity theft. Blockchain introduces a new way of managing digital identities by providing users with control over their personal information. Instead of storing sensitive information on a centralized server, blockchain allows users to store their data in an encrypted, decentralized manner. Access to this information is granted through cryptographic keys, ensuring privacy and security.
4. Challenges of Blockchain in Digital Security
While blockchain offers robust security features, it’s not without its challenges:
- Scalability: As more transactions are added to the blockchain, the size of the ledger increases, potentially slowing down the network. Finding a balance between security and scalability is an ongoing challenge.
- Energy Consumption: Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) are computationally intensive, consuming significant amounts of energy. This raises concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain.
- Regulatory and Compliance Issues: Blockchain’s decentralized nature poses challenges in terms of regulation and compliance. Governments and institutions are still figuring out how to integrate blockchain into existing legal frameworks.
5. The Future of Blockchain in Digital Security
Despite its challenges, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize digital security. Innovations like:
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: A cryptographic method that allows one party to prove to another that a statement is true without revealing any information beyond the validity of the statement. This concept can greatly enhance privacy and security in blockchain applications.
- Blockchain Interoperability: Solutions that enable different blockchain networks to communicate and share information securely. This will facilitate data sharing across platforms while maintaining high-security standards.
Blockchain’s role in securing digital transactions, managing identities, and verifying the integrity of data is likely to expand as industries continue to adopt this technology. Its application in fields like finance, healthcare, supply chain, and cybersecurity shows immense promise in making our digital world more secure and transparent.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain technology offers a new paradigm for digital security, providing a decentralized, transparent, and highly secure method for recording and verifying transactions. Its unique features like immutability, encryption, and decentralization make it a powerful tool for combating fraud, enhancing privacy, and ensuring data integrity. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in blockchain technology are paving the way for a more secure digital future.

%20with%20a%20shield%20symbol,%20high.webp)




0 Comments